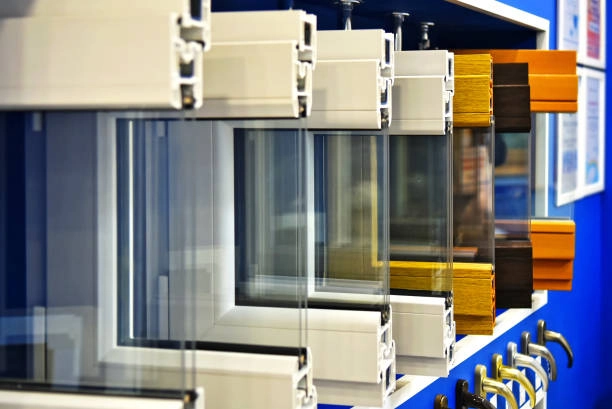
Glass isn’t just a clear barrier or a simple window anymore. In today’s building designs, it works as a supporting part, an efficient layer, and a bold look. It changed from breakable stuff to an advanced piece. This shift has changed how structures connect with people and nature. Be it clear fronts or weight holding steps, glass mixes shape, use, and new ideas closer than before.
Key Innovations Shaping the Use of Glass in Modern Architecture
In recent years, building glass has changed a lot. This happened because of new ideas like laminated glass, tempered glass, and insulating glass units. These things made glass safer and more useful.
Laminated glass, for instance, gets made by putting a layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) between two or more sheets of glass. This setup keeps the glass together even if it breaks. So, it boosts safety and cuts down on hurt risks. Tempered glass gets treated with heat or chemicals to make it much stronger than regular annealed glass. Insulating glass units (IGUs) join several panes with a spacer in between. They seal it up to cut down heat move, which helps save energy.
These big steps let builders use huge areas of glass without losing good results. They allow creative builds and green practices too.
Transparent Facades in Contemporary Design
Architectural Benefits of Transparent Glass Facades
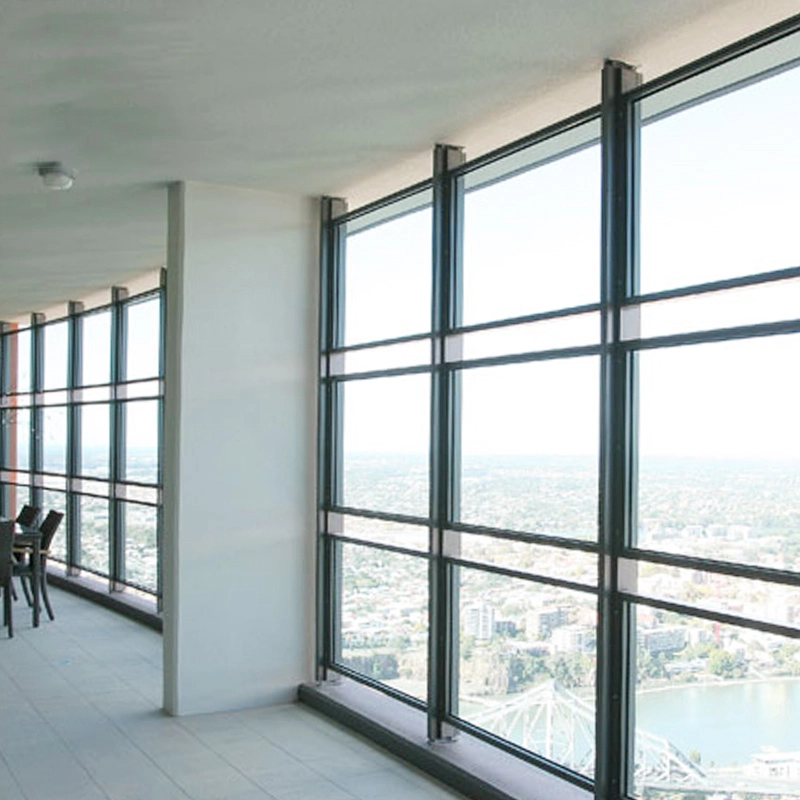
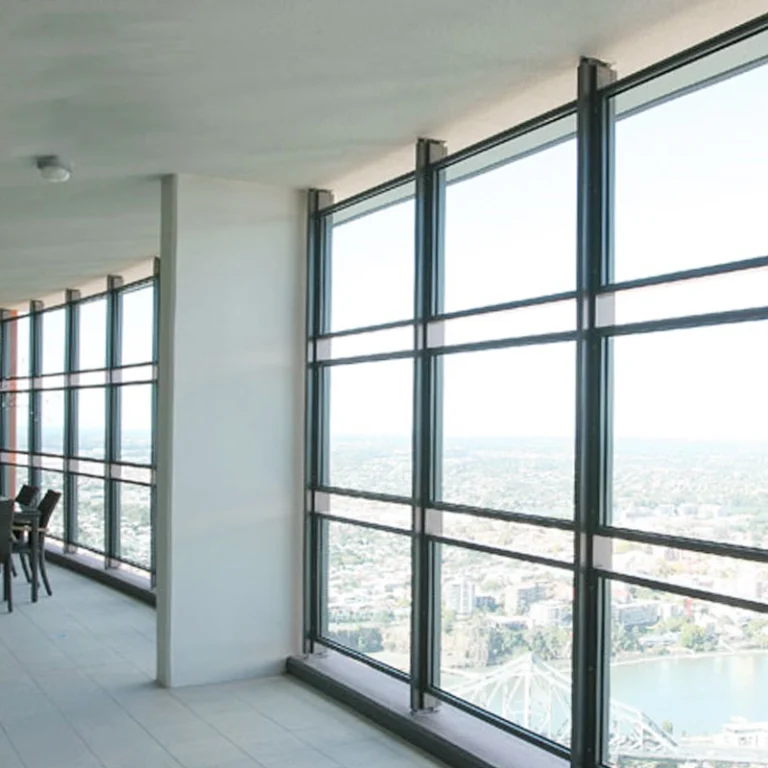
Clear fronts let buildings open up to what’s around them. This boosts light from the sun inside. It also links indoor spots with outside areas. Glass fronts pull natural light far into structures. They make folks inside feel better. Plus, they cut the need for fake lights during day time.
They give buildings a smooth, fresh appearance too. This style shows up in office high rises and culture spots.
Structural and Performance Considerations
But looks aren’t everything. Clear fronts have to meet tough build rules, especially in tall spots or shaky ground areas. That’s where tempered and laminated glass help out. Laminated types give better hit resistance and safety. Tempered kinds offer the power to handle wind push and heat strain.
When you pair them with low emissivity coatings and IGUs, these fronts deliver solid warmth control while keeping things see through.
A pro supplier like Landson Glass, a focused maker of building glass options, can tweak these setups to hit exact work goals—be it for energy scores or sound needs.
The Role of Glass Curtain Walls in Modern Buildings
Functional Advantages of Curtain Wall Systems
Curtain walls are outer walls that don’t carry weight. They hang from a building’s frame like a drape—that’s why the name. Often, they use big panes of insulating glass units set in aluminum frames.
Their useful perks include:
- Weather shield: Curtain walls block wind and rain.
- Heat control: IGUs keep indoor temps steady.
- Adaptability: Panels get shaped, sized, and cleared as needed.
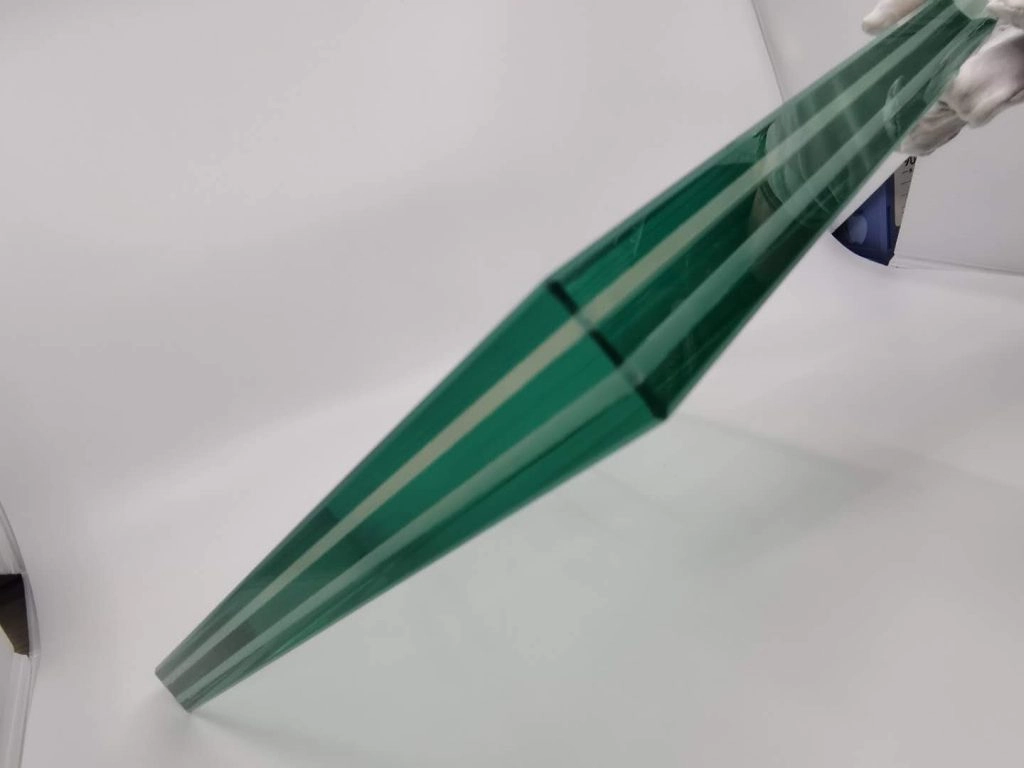

Material Innovations in Curtain Wall Construction
Current curtain wall plans often mix strong laminated or tempered glass to match new safety rules. Laminated panels can have layers that stop UV rays or quiet down noise.
Frame setups got better too—thermal breaks and seals now boost the curtain wall’s energy saving. This aids buildings in getting marks like LEED.
Landson Glass backs curtain wall jobs by providing exact made tempered, laminated, and IGU panels fitted to build specs.
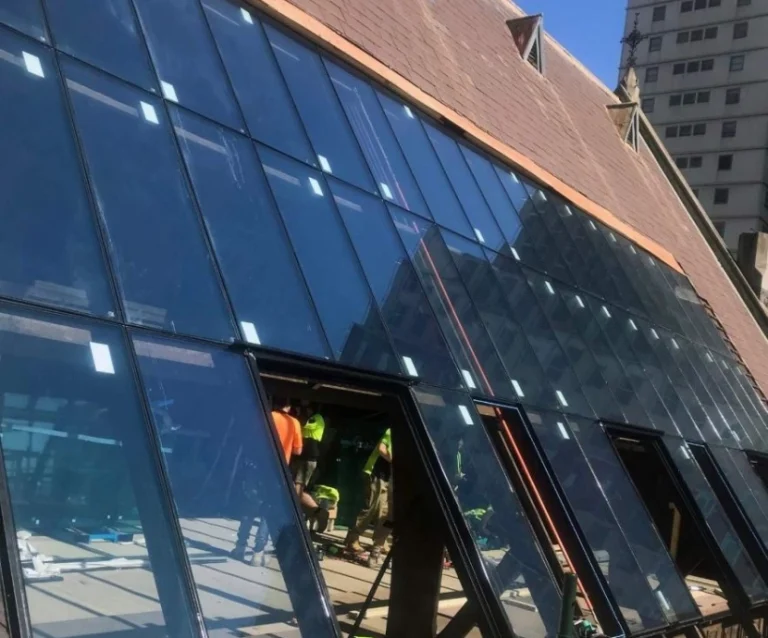
Skylights and Roof Glazing Solutions
Enhancing Interior Spaces with Overhead Glazing
Top glazing—like skylights and roof lights—adds space and brightness inside. These parts pour daylight into areas. They can slash energy use a bunch when planned right. They’re extra handy in big work buildings or open halls where side windows are scarce.
Skylights offer chances for build wow too—picture museums or art spots where light shapes how visitors feel.
Technical Aspects of Roof Glazing Installations
Safety comes first with top glazing. Laminated glass often gets picked because it stays put even if smashed. For places with hail or heavy snow, tempered laminated mixes work best.
Roof glazing setups must seal tight and keep warmth. IGUs with argon gas inside and low E coatings get chosen for this.
Interior Glass Partitions for Open Plan Environments
Design Flexibility with Interior Glazing Systems
Inside dividers from glass keep things open to see while making separate zones in offices or work insides. These can have sliding doors, framed bits, or even changeable privacy glass.
Their plan bend lets them fit into most setups without messing up views or light spread.
Acoustic and Privacy Solutions in Glass Partitions
Current laminated glass can get made with sound blocking layers that drop noise pass a lot—key in open work spots where private talks matter.
Etched surfaces, decor films, or smart glazing tricks can boost privacy without losing light.
Glass Staircases and Railings as Structural Features
Visual Impact of Transparent Vertical Circulation Elements
Glass steps and guards show up often in fancy work and home buildings. Their light feel lets other build parts stand out while still working well.
Step surfaces made from thick laminated tempered glass usually have no slip textures or covers for safety.
Safety Measures in Load Bearing Glass Applications
Weight carrying uses need top strength. Here, multi layer laminated tempered glass is a must. The layers not only hold broken bits but also take the weight if one fails.
Handrails often blend in using steel fittings that skip drilling into the glass—keeping it whole.
Advancing Architectural Expression Through Building Glass Innovation
From bent glazing to printed designs on glass, new ideas have stretched plan limits. Builders can now add special feels, shades, and work traits to fronts or insides without hurting safety or green goals.
What seemed tough before—like full clear support walls—is now regular thanks to steps in tempered, laminated, and insulating ways.
Teaming with skilled makers like Landson Glass makes sure designers snag not just the right item but solid tips for each job—from specs to drop off.
FAQ
Q1: What’s the difference between tempered and laminated glass?
Tempered glass is heat treated for strength; laminated glass sandwiches layers for safety even when broken.
Q2: Why use insulating glass units (IGUs)?
IGUs improve thermal insulation by trapping air or gas between panes, reducing heat loss or gain.
Q3: Are glass facades energy efficient?
Yes—especially when using low E coatings and IGUs tailored for thermal control.
Q4: Can you use glass structurally?
Absolutely. With proper lamination and treatment, glass can serve as floors, walls, even stairs.
Q5: What makes Landson Glass different from other suppliers?
Landson Glass offers not just products but complete custom solutions—from tempered panels to decorative laminates—for architectural projects worldwide.