Laminated Glass in Modern Architectural Design
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Laminated glass gets made by sticking two or more sheets of glass with interlayers, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA). This setup boosts the material’s toughness. Plus, if it breaks, the pieces stick to the interlayer. That cuts down on injury chances and keeps some wholeness.
The lamination process really helps improve the glass’s strength and safety. Interlayers affect main traits like clear sight, sound reduction, and UV blocking. For instance, Landson Glass makes top notch laminated items using two modern laminating lines. They ensure steady quality and results for all sorts of uses.
Key Architectural Applications
Laminated glass serves as a top choice in various building styles. Its durability and see through look fit well for:
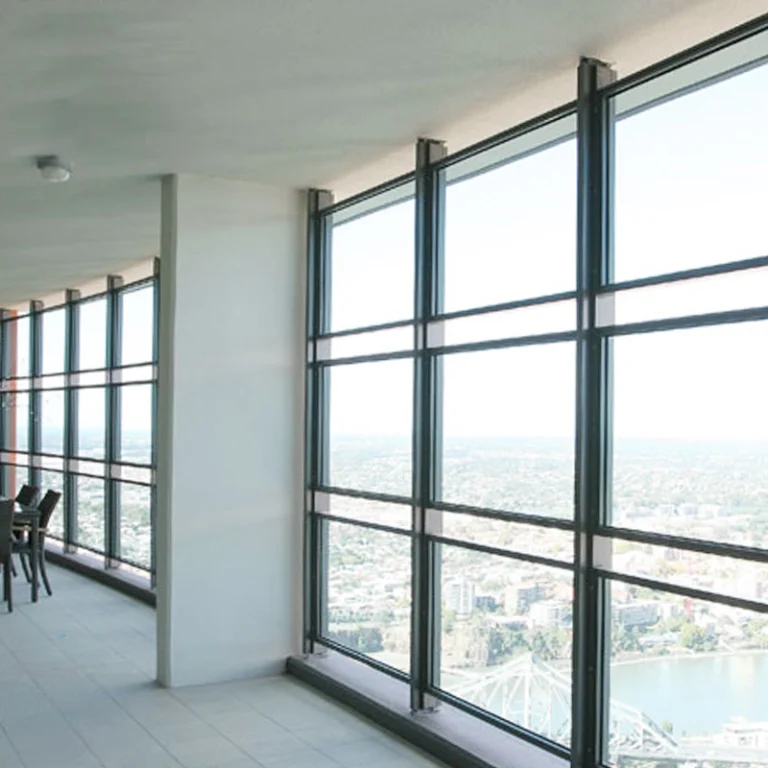
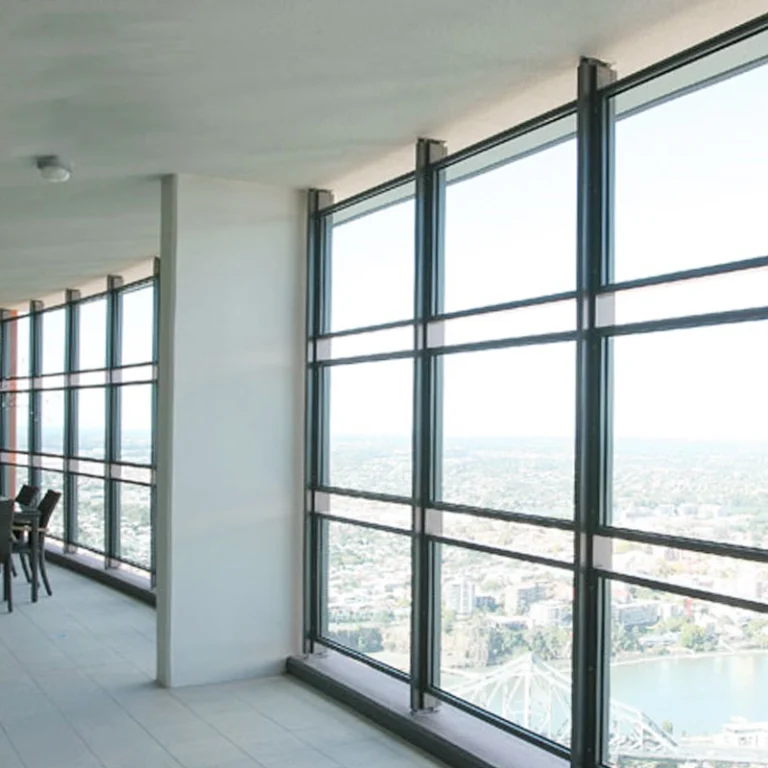
- Curtain walls and façades
- Skylights and overhead glazing
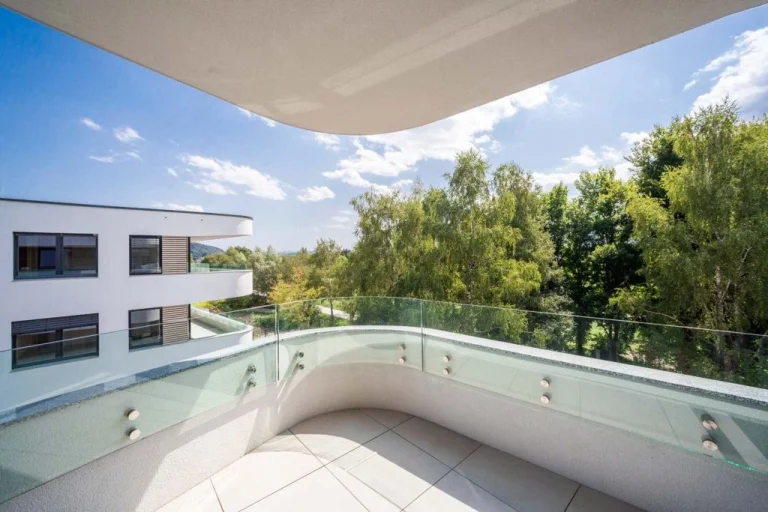
- Stair balustrades and glass railings
Its safety perks shine in slanted or ceiling setups. There, breaks could cause big dangers. In today’s buildings, laminated glass aids tricky shapes and open designs. It keeps safety and looks intact.
Performance Benefits Beyond Safety
Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
In busy city spots, noise issues never stop. Laminated safety glass fights this with interlayers that soak up sound waves at different pitches. Acoustic PVB interlayers aim just for that. They bring better quiet in places like hospitals, offices, and homes.
Enhanced Security Features
Laminated glass boosts protection thanks to its built up layers. Even after shattering, it stays whole. That slows down break ins and gives time to react. Banks, shops, and risky spots often pick it for this reason.
| Feature | Benefit |
| Multi layered structure | Resists forced entry |
| Post breakage integrity | Retains shape, deters intrusion |
| Tamper resistant glazing | Suitable for high security applications |
UV Protection and Material Preservation
One not so well known plus is its UV stopping power. Laminated glass blocks over 99% of bad ultraviolet rays from the sun. So, it guards inside items from color loss. This matters a lot in spots like museums, stores, or rooms with prized decor or art.
Aesthetic Flexibility in Design
Laminated glass mixes use with style well. It comes in many shades, hues, designs, and surfaces for eye appeal. Architects can pick it to match brands or boost themes. Choices like silkscreen frit patterns and digital printing let folks add custom images or feels right into the glass.

Structural Advantages in Architectural Systems
Load Bearing Potential with Laminated Glass
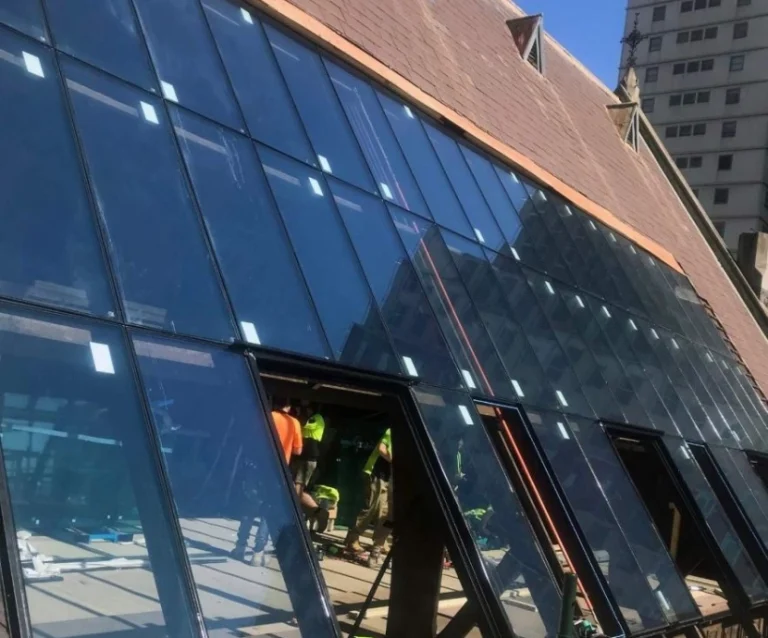
New ideas in glass building have made laminated panels key weight holders in structures. Paired with tempered glass sheets and planned right, they work for:
- Glass floors
- Structural fins
- Cantilevered staircases
The interlayer aids in sharing loads after a break. This meets tough building rules. It also allows simple, clean looks.
Durability Under Environmental Stressors
Laminated safety glass stands up great to weather pressures like wind pushes, heat changes, and shakes from quakes. It handles thermal strain, wind forces, and seismic shakes well. Also, made in controlled spots with care, the chance of layers peeling drops a lot.
Integration with Other Glazing Technologies
Compatibility with Insulating Glass Units (IGUs)
To boost heat control without losing safety or sound blocking, laminated sheets often join IGUs. This mix gives all around wall systems that:
- Lower U values
- Maintain noise control
- Improve occupant safety
These fixes help a ton in office high rises or public buildings aiming for LEED points.
Synergy with Smart Glass Solutions
Laminated safety glass pairs nicely with switchable smart tech. That tech changes light pass through on demand. It can layer with solar cells too, making walls that catch energy. This idea picks up speed in green building work.
Considerations for Specification and Installation
Thickness Options Based on Application Requirements
Laminated glass offers different thicknesses for load and size needs. Thickness 6.38–33.04mm choices cover from pretty dividers to strong floors.
| Application Type | Suggested Thickness |
| Internal partitions | 9.52–13.52 mm |
| Balustrades | 17.52–21.52 mm |
| Structural floors | 25.52–33.04 mm |
Keep in mind, thicker sizes raise hit resistance. But they add weight for handling and support needs.
Compliance with Building Codes and Standards
Laminated glass needs to match strict rules like ANSI Z97.1 or EN 12600. Teaming with approved makers like Landson guarantees this. Climate controlled facilities produce world class Safety Glass, fully compliant to meet Australian, New Zealand standards and European standards.
Industry Expertise Supporting Project Success
Role of Specialized Suppliers in Custom Solutions
Quality stuff and exact making are musts in building glass work. Landson Glass Supplies High Quality, SAI Global Certified Laminated Stock. They provide:
- Multi laminated options
- Custom tinting (Grey, Bronze, Blue)
- Full edgework and drilling services
Working early with skilled makers helps match looks goals with real world fit.
Material Innovation Driving Design Possibilities
New steps in interlayer tech keep opening up building uses. Landson backs this with research driven products and advice on designs. It helps builders stretch ideas while sticking to real results.
Sustainability Contributions of Laminated Glazing Systems
Energy Efficiency Through Solar Control Options
Sun control interlayers cut heat buildup without messing up natural light plans. This raises comfort inside. It also saves power on cooling systems. Such helps projects score LEED credits.
Lifecycle Benefits Supporting Green Building Goals
Laminated glass lasts long if set up right. Its parts can get reused when taken apart with care. That fits round economy aims and cuts lasting harm to nature.
Future Trends in Laminated Glass Applications
Expanding Role in Structural Glazing Systems
No frame building styles keep growing. Here, laminated structural glass acts as a main weight carrier. It drops heavy frames and boosts clear views.
Integration into Adaptive Façade Technologies
Smart walls that adjust to weather changes lean on stacked materials. Laminated safety glass makes a key part in these top setups. It balances light, warmth hold, and quick changes.
Landson Glass continues to support innovative applications by offering precision engineered laminated glass solutions tailored for evolving architectural needs across global markets.
FAQs
Q: What is the main difference between laminated and tempered glass?
Tempered glass shatters into small pieces upon impact; laminated glass holds together due to its interlayer structure.
Q: Can laminated glass be used for soundproofing?
Yes, especially when acoustic PVB interlayers are used—it’s effective at reducing noise across various frequencies.
Q: Is laminated glass suitable for exterior applications?
Yes, it performs well under environmental stressors like wind loads and UV exposure when manufactured to high standards.
Q: Does laminated glass offer UV protection?
Yes, it blocks over 99% of harmful UV rays, preserving interiors from fading.
Q: Can laminated glass be customized for decorative purposes?
Absolutely—options include colored interlayers, digital printing, frit patterns, and rice paper embedding for visual enhancement.