Structure and Composition of Vacuum Insulated Glass
Core Components of Vacuum Glass
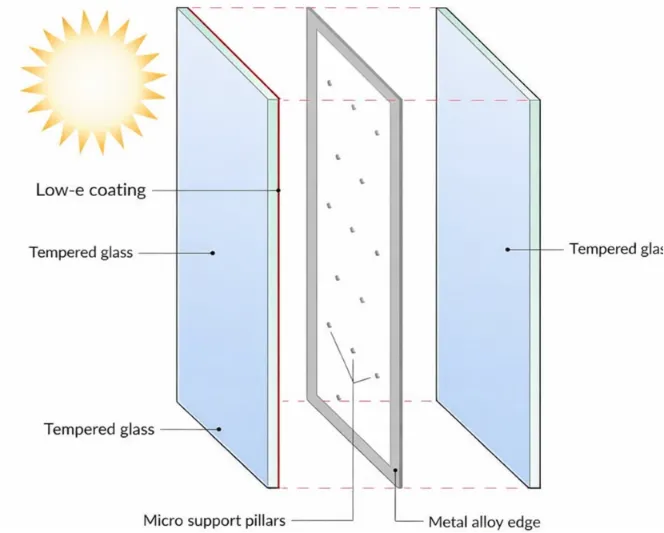
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes. They are separated by a small vacuum gap. This vacuum stops most heat transfer ways. It blocks convection and conduction through air. As a result, it saves a lot of energy. Tiny support pillars sit between the panes.
They keep the space even. These pillars are very small. They do not block the view. Around the edges, seals hold everything together. They keep the vacuum tight for many years. This stops air and water from getting in.
The Role of Low E Coatings in Vacuum Glazing
Low emissivity (Low E) coatings boost vacuum glass performance. These thin films bounce back infrared heat into the room. They cut down heat loss during cold months.
At the same time, they let in plenty of light. Builders often put them on one or both inside surfaces. This setup balances warmth and daylight well. It keeps rooms cozy. Plus, it does not reduce clear sight.
Comparison with Conventional Insulated Glass Units
Vacuum glazing beats regular insulated glass units (IGUs) in key ways. Check the table below for details:
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass | Conventional IGU |
| Thickness | 6–10 mm | 20–28 mm |
| Thermal Performance (U factor) | ≤ 0.4 W/m²K | ~1.1–2.8 W/m²K |
| Gas Fill Requirement | None | Argon/Krypton filled |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Longevity | 20+ years | 10–15 years |
VIG gives the same or better heat control. Yet it uses a much slimmer shape. It skips the need for special gases. Those gases can wear out in old IGUs over time.
Functional Advantages of Vacuum Insulated Glass
Thermal Performance and U Factor Efficiency
The U factor shows how a window holds in heat. A smaller number means stronger insulation. Vacuum insulated glass reaches U factors down to 0.4 W/m²K. It can do better than some triple glazed setups.
This works great in very hot or cold places. It keeps inside temps steady. And it cuts down on energy use.
Acoustic Insulation and Noise Reduction Benefits
Besides heat control, VIG handles sound well. The vacuum gap blocks noise waves. It stops them from passing between panes. So, it suits noisy spots like busy streets or airports. Or even roadsides. In shops or homes, it creates calmer spaces inside.
Slim Profile and Weight Reduction Benefits
Vacuum glass has a super thin build. This fits easy into new designs or old fixes. It does not add extra bulk or pounds. The light weight makes setup simpler. It works with narrow frames too. Designers get more options. They do not lose out on warmth or strength.
Applications of Vacuum Glazing in Modern Architecture
Integration into New Construction Projects
Vacuum glazing shows up more in energy saving builds. It fits green designs too. It helps get LEED ratings by improving heat barriers. This lowers building energy needs. You can use it in walls, roof windows, or front glass. It works for all kinds of jobs.
Use in Renovation and Retrofit Projects
Adding VIG to old buildings boosts heat savings a ton. It does this without big changes to the structure. For old sites that look special, the thin glass fits old frames. It keeps the historic look. This way, you update to new energy rules easy.
Bird Safe Glass Options within Vacuum Glazing Systems
Today’s vacuum glass can add bird friendly parts. They use patterns or UV shine to stop bird hits. Humans still see clear through them. These add ons blend in. They do not hurt the heat hold or strength.
Material Innovation and Customization Possibilities
Architectural Glass Variants for Specialized Needs
Vacuum insulated glass comes in different types for special jobs:
- Tempered for extra toughness
- Laminated for safety or quiet
- Decorative with colors, designs, or feels
You can get custom sizes and shapes too. They match tricky plans.
The Role of Landson Glass in Architectural Projects
Landson Glass makes custom vacuum glass for looks and function. They supply many types like tempered, laminated, and insulated. Their team helps builders with advice and exact making. Landson products go into offices, schools, and fancy homes.
Durability, Lifespan, and Maintenance Considerations
Long Term Performance of Vacuum Insulated Units
Smart edge seals let vacuum units keep their pull for years. They fight off water, air shifts, and wet buildup. These are weak spots in regular IGUs. With less parts to break, VIG needs little care after setup.
Environmental Impact and Energy Savings
VIG skips heavy layers and gases. So, making it uses fewer stuff. This means less carbon from the start than triple glass. Over time, it cuts heating and cooling needs. That lowers building pollution. It matches green building goals for less energy and carbon.
FAQs
Q: What makes vacuum insulated glass different from regular double glazing?
It uses a vacuum layer instead of gas fill between panes, offering better insulation in a thinner profile.
Q: Can VIG be used in cold climates?
Yes, its low U factor makes it ideal for extreme temperatures, retaining heat more efficiently than traditional options.
Q: Is vacuum glass heavier than conventional insulated glass?
No, it’s usually lighter due to its thinner structure and lack of gas filled chambers.
Q: Does Landson Glass provide custom sized vacuum glazing?
Yes, Landson Glass offers tailor made solutions including size, shape, coating, and decorative finishes.
Q: Are bird safe options available with vacuum insulated glass?
Yes, visual patterns can be incorporated to prevent bird collisions while maintaining clear views.