Laminated Glass Thickness: Strength and Optical Performance
How Thickness Contributes to Structural Integrity
Laminated glass consists of two or more sheets of regular glass joined with interlayers. These interlayers are usually PVB or other plastics. Thickness matters a lot for the strength of these units. In simple terms, the thicker the laminated glass, the better it stands up to hits and physical pressure.
Adding more interlayers boosts the ability to stop penetration. This feature is key in places where glass needs to handle break ins, explosions, or even gunshots. Multi laminated choices, like those from Landson Glass, let you pick thickness based on the protection level you want.
For building uses, usual laminated glass thickness goes from 6.38 mm to 33.04 mm. It fits both home and business needs.
How Glass Thickness Affects Visual Clarity
Safety and looks often clash a bit. Thicker laminated glass might let in a tad less light. This depends on the interlayer’s type and shade. For instance, colored or textured interlayers can soak up more light than clear ones.
To cut down on visual issues like blur or ripples, careful making methods are vital. Makers like Landson Glass create top notch laminated items with two modern laminating lines. These ensure clearness and evenness in big panels.
Finding the right mix of see through quality and safety means picking the right glass thickness. It also involves selecting fitting interlayer stuff and making ways.
Application Based Considerations for Laminated Glass Thickness
Residential and Commercial Façades
In façades—such as windows, curtain walls, or doors—people pick laminated glass for its safety and work features. Common thicknesses run from 6.38 mm to 17.52 mm for houses. Business spots might need up to 21.52 mm or thicker because of bigger loads.
Aside from not breaking easy, laminated glass helps block sound and UV rays. Sound reducing interlayers cut noise in city spots. And they don’t harm the visual side.
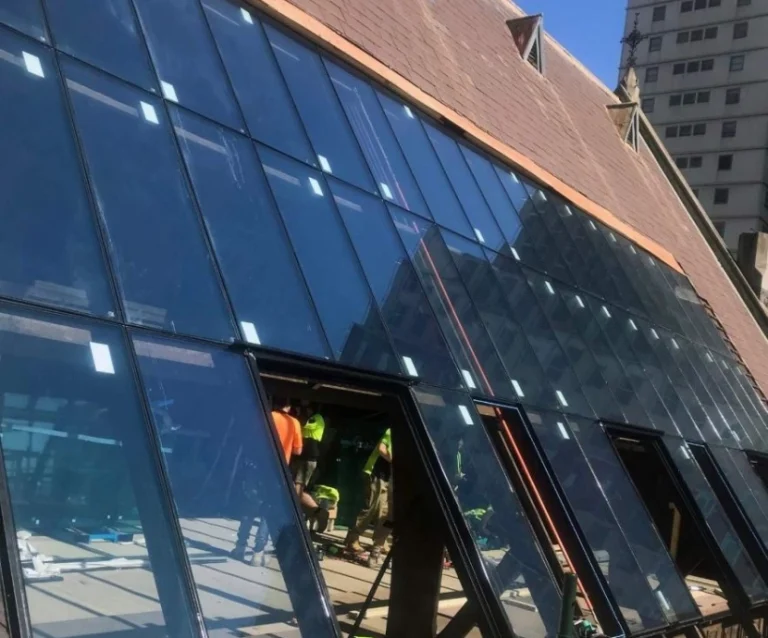
Overhead Glazing and Skylights
Skylights and other roof setups require thicker laminated glass for safety. Protection from dropping items is a must. So is following local rules that set minimum glass thickness and interlayer toughness.
Thicknesses of 17.52 mm and above are often picked here. This is true especially in spots with harsh weather or earthquakes.
Automotive Glazing Requirements
Car windshields mostly use laminated glass with standard thicknesses around 6.76 mm to 7.52 mm. The main aim is safety in crashes. The interlayer keeps the glass in one piece after a hit. This lowers the chance of sharp bits flying around.
Side windows in fancy cars are starting to use laminated builds more. They add sound blocking and break in resistance.
Safety and Security Applications
Security needs differ a lot—from stopping theft to handling blasts or bullets. For these, suggested laminated glass thicknesses can go over 25 mm. It depends on the danger level.
Advanced setups might use several glass layers and interlayer mixes. They fit well with sensors or alarms for better guarding.

Factors That Influence Laminated Glass Thickness Selection
Building Code Compliance and Regional Standards
Choosing the right laminated glass thickness begins with knowing the rules that apply. World standards like EN (Europe), ASTM (USA), and GB (China) give basic needs for hit resistance and load holding.
Local building codes often set minimum thicknesses. This depends on height from the ground, spot, and who uses it. So, it’s smart to talk to project engineers early in planning.
Environmental Load Conditions and Risk Assessment
Wind forces in tall buildings, earthquake areas, or crowded spots all affect laminated glass choices. Engineers check these along with people impact cases—like falls or bumps. They figure out safe setup details.
Each project needs its own check. What fits a city office tower might not work for a beach house.
Acoustic Performance Requirements
In loud places like airports or city hubs, thicker laminated glass with sound interlayers boosts noise blocking.
Thicker PVB or special sound films stop shakes better than regular ones. This makes laminated glass a top pick over single sheets or basic double glazing in quiet needed spots.
Material Composition and Interlayer Variations
Role of PVB Interlayer Thickness in Performance Outcomes
PVB (polyvinyl butyral) is the go to interlayer in building laminated glass. Usual PVB thicknesses are 0.38 mm, 0.76 mm, and 1.52 mm. Thicker ones help with more hit resistance or noise control.
The interlayer’s thickness changes its bendiness and stickiness. These are big for lasting under strain.
Alternative Interlayers: EVA, SGP
Different interlayers fit different jobs:
| Interlayer Type | Key Features | Best Use Cases |
| PVB | Flexible, good adhesion | General architectural use |
| EVA | UV stable, moisture resistant | Decorative panels |
| SGP | Rigid, high strength | Structural glazing |
Rice paper laminated glass is a kind of decorative glass design but with safety laminated glass, with the rice paper internally with EVA lamination method. This shows how pretty goals can pair with safety using EVA lamination.
Industry Testing Protocols for Laminated Glass Thickness Validation
Mechanical Load Testing Methods
Mechanical tests make sure laminated glass works in real life setups:
- Pendulum tests mimic body hits.
- Ball drop tests check resistance to falling stuff.
- Static load testing copies wind or pressure over time.
These tests check interlayer work and total panel power.
Optical Quality Evaluation Standards
How it looks matters as much as how strong it is. Laminated glass has to meet rules for:
- Light transmittance (ISO compliant)
- Haze levels
- Distortion control
- Color consistency
Integrating Laminated Glass into Architectural Projects with Confidence
Collaboration with Specialized Suppliers During Design Phase
Talking with skilled suppliers early leads to better results. They help pick interlayers and custom thicknesses. This avoids expensive changes later.
Landson Glass makes high quality laminated products using two state of the art laminating lines. They guide architects and builders with tech tips and rule checks.
Customization Options Based on Project Specifications
Laminated glass offers more than just strength. It can be adjusted for looks and function:
- Mix with tinted or Low E coatings
- Add pretty bits like silkscreen frit patterns
- Put in insulating layers for energy saving
Future Trends in Laminated Glass Development
Innovations in Lightweight High Security Laminates
New stuff like ionoplasts allows thinner but tougher laminated panels. These changes help in cars and super tall building fronts. Weight cuts matter there, yet safety stays strong.
Sustainability Considerations in Material Selection
Eco building pushes for green picks. Landson Glass backs green efforts with new materials. This includes reusable interlayers and energy smart making ways.
FAQs
Q: What is the standard laminated glass thickness for residential windows?
Typically between 6.38 mm and 17.52 mm depending on local codes and design needs.
Q: Does thicker laminated glass always provide better sound insulation?
Yes, especially when paired with acoustic PVB or specialized damping films.
Q: Can laminated glass be both decorative and safe?
Absolutely. Options like rice paper laminates combine aesthetics with EVA based safety lamination.
Q: Is multi laminated glass necessary for high security areas?
Yes, multi layer configurations provide higher resistance to impact, blast, and intrusion.
Q: Does Landson Glass offer customized laminated solutions?
Yes, Landson Glass offers full service fabrication from cutting to lamination, supporting project specific requirements efficiently.