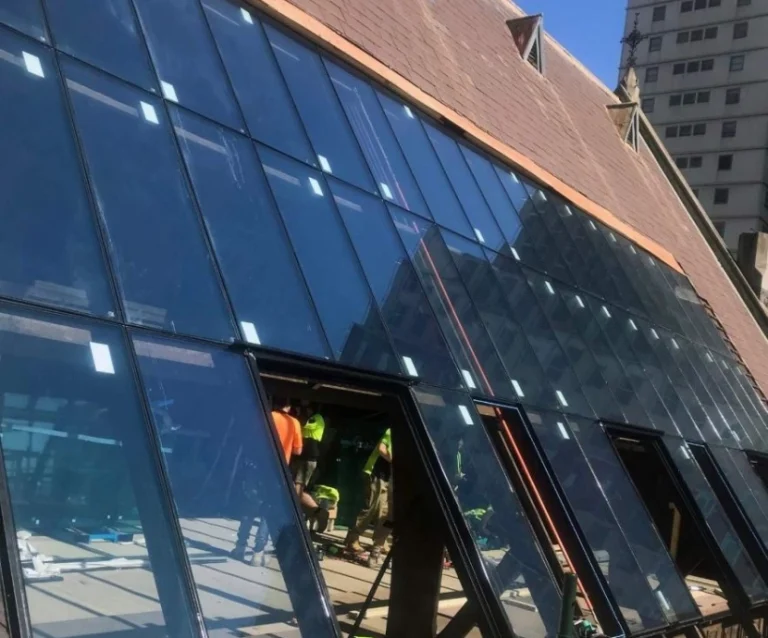
Smart glass technology has shifted from just an idea to a key part of today’s buildings. It used to seem like something from the future. Now, these clever materials change how people deal with light, room layouts, and personal space in homes, shops, and public spots.
What Is Smart Glass Technology
Core Principles of Switchable Glass
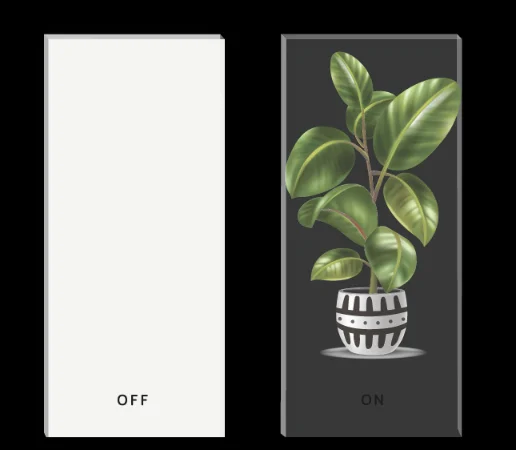
Smart glass, sometimes called switchable glass or glass tech, can change how it handles light when electricity is added. It switches from see-through to foggy, or from clear to shaded, based on what the user wants or on automatic setups.
This change works both ways. Plus, people can control it exactly, either by flipping a switch or using computer systems for buildings.
Primary Types of Smart Glass Technologies
Several main kinds of smart glass exist.
- Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC): This one focuses on privacy. It turns foggy without power and clear with power.
- Suspended Particle Devices (SPD): It reacts quickly to electricity for adjusting light levels.
- Electrochromic Devices (ECD): This provides slow shading through chemical changes. It saves energy well.
Each type fits different needs, like how fast it works, how clear it gets, or how much power it uses.
Formats and Integration Options
Smart glass fits into various forms.
- Adhesive switchable film: You stick it right on old glass to update things.
- Laminated triplex smart glass: This works for new builds. It has switchable layers sandwiched between glass sheets.
- Insulated Glass Units (IGU): It mixes smart layers into double or triple glass for better heat control.
How Smart Glass Works in Practice
PDLC uses tiny liquid crystal drops in a plastic base. Without power, these drops scatter light. That gives a misty look. When you add voltage, the crystals line up. Then light passes right through.
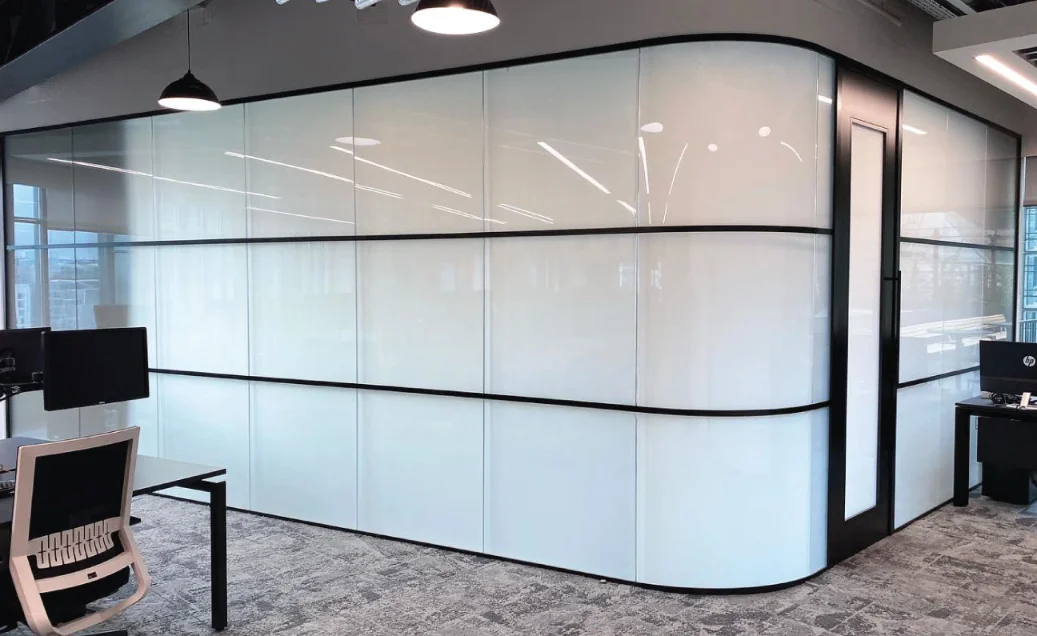
This tech shows up a lot in places like office walls, meeting rooms, and shower areas. It’s handy and not too pricey for inside spots where you need quick privacy.
| Feature | PDLC | SPD |
| Switching Speed | Fast | Very Fast |
| Power Use (During State) | Power to stay ON | Power to stay ON |
| Best For | Privacy | Light Control |

Architectural Applications of Smart Glass
Offices and Commercial Buildings
Smart glass walls let open offices turn into private areas right away. No need for real walls. You keep natural light flowing. That boosts teamwork and quiet work alike.
Residential Spaces and Interiors
In houses, smart glass takes over from old curtains or shades in sleeping rooms and baths. Folks like it in simple styles that skip messy looks. It blends nice views with real use.
Hospitality and Healthcare Environments
Hotels put switchable glass between beds and baths for a smooth stay. Hospitals need privacy too. Smart glass keeps things clean without dusty cloth covers that hold germs.
Retail Storefronts and Public Spaces
Shops use glass that goes from clear show windows to solid safety shields at night. Some even project images for ads. That mixes business signs with real work.
Benefits That Transform Modern Architecture
Privacy Control Without Physical Barriers
Smart glass lets people pick when to hide or show without clunky tools.
- It skips blinds or curtains.
- It keeps rooms feeling wide open.
- It improves looks in spots where folks can see in.
Energy Efficiency and Light Management
Smart glass tweaks how much light gets in based on sun levels. As a result, it cuts down on air conditioning or heating needs.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Integration
Smart glass comes flat, bent, or with pretty designs. It fits many frame types. Builders can keep sleek shapes while adding smart features.
Acoustic Performance and Cleanliness Advantages
Laminated smart glass cuts noise too. That helps in loud places like clinics or work spots. Smooth surfaces wipe clean easy. They’re great for clean areas like hospitals.
Material Considerations in Specifying Smart Glass
Choosing Between Film vs Laminated Glass
| Aspect | Adhesive Film | Laminated IGU |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Higher initial cost |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Insulation | Limited | Excellent |
| Retrofitting | Ideal | Not suitable |
Film suits updates well. Laminated IGUs work best for fresh builds or lasting jobs.
Installation Requirements Across Project Types
Setting up needs some thought.
- Wires for power have to go in or stay reachable.
- Film sticks best on flat, even surfaces.
- Laminated pieces need planning early in the window design.
Cost Factors and Long-Term Value
Price Influencers Across Technologies
A few things set the price.
- The tech type, like PDLC, SPD, or ECD.
- How big or what shape the pieces are.
- The controls, whether simple switches or smart auto ones.
- Special tweaks, like bends or printed marks.
Big shop projects get cheaper per piece with lots ordered.
Operational Efficiency Over Time
Smart glass beats old shades that break or get dirty. It has few parts that move. So upkeep stays low. It sips power too, mainly the electrochromic kind that only needs it to shift.
The Role of Smart Glass in Sustainable Design Trends
Integration With Building Automation Systems
Smart glass links up with sun trackers, clocks, or people counters. Buildings can then tweak the clearness on their own based on what’s happening now.
Contribution to Green Building Certifications
It aids in things like.
- Cutting electric lights.
- Grabbing free sun heat in cold times.
- Keeping out heat in warm spells.
All that pushes green goals and makes folks comfy.
Industry Insights From Manufacturing Experts
Architectural Collaboration From Concept to Completion
Working early with makers like Landson Glass picks the right stuff for your aims. Landson Glass understands customers requirements with a focus on product quality and customer satisfaction.
Their team helps from the first idea to setup details.
Customization Capabilities for Unique Projects
Landson Glass makes special items, like patterned or bent ones. They supply many types, from strong to heat-saving, for all sorts of building needs.
Future Directions in Smart Glass Technology
Emerging Innovations on the Horizon
Studies look at mixes, like PDLC privacy with electrochromic shade. No-wire controls come next for easy adds to old spots.
Market Expansion Across Sectors
Smart glass heads beyond homes to planes, trains, display halls, and schools. Anywhere you want rooms that change easy.
Landson Glass, a long established and highly trusted glass processor, has been servicing the glass and glazing industries in Australia, New Zealand and many other countries since 2002.
FAQs
Q: Can switchable film be applied to any existing window?
Most clear flat-glass surfaces are compatible, though proper surface preparation is key.
Q: Does smart glass block UV rays?
Yes. Many types block up to 99% of UV radiation even when transparent.
Q: Is there a delay when switching states?
PDLC reacts nearly instantly; electrochromic types take longer but use less power overall.
Q: Can smart glass be customized in shape?
Yes. Manufacturers like Landson Glass offer curved panels and custom patterns for design flexibility.
Q: Is smart glass suitable for outdoor façades?
Absolutely—with IGU formats offering both weather resistance and insulation performance.